Heat Pump Replaces Steam Boiler to Reduce Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Taking a leap towards sustainability! Daikin Industries is swapping steam boilers with innovative heat pumps to slash carbon emissions as a move to cleaner, greener energy solutions.
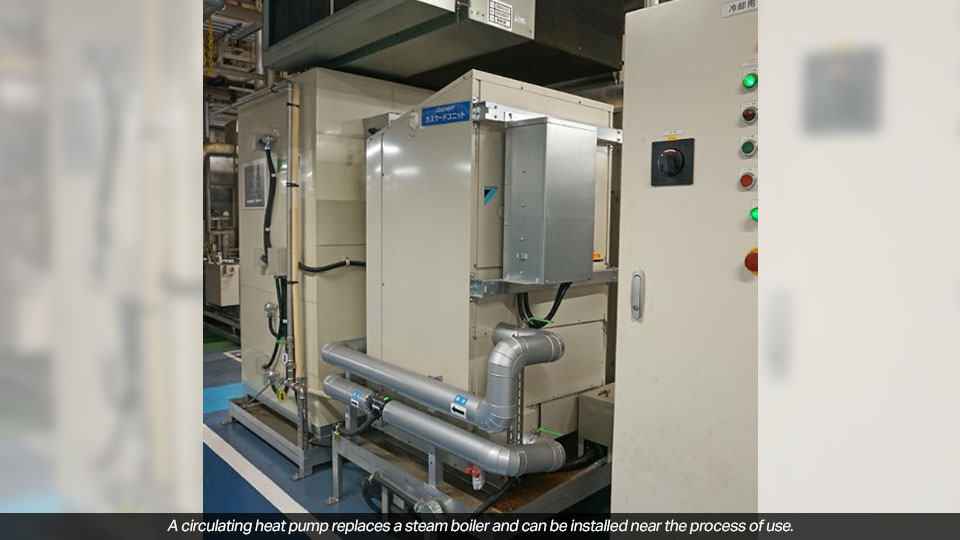
Japan, 2 November 2023 - Daikin Industries, Ltd., will gradually replace industrial steam boilers at its factories with heat pumps in an effort to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions during production processes. First, at the Rinkai Factory in Sakai City, they installed a self-developed circulating heating heat pump that produces hot water of up to 80 degrees Celsius in two painting lines in place of a boiler. It is expected to reduce annual CO2 emissions by 86% and running costs by 82%. In the future, the company will consider expanding to other bases such as the Shiga Plant (Kusatsu City, Shiga Prefecture).
In aiming to achieve carbon neutrality (virtually zero greenhouse gas emissions) at the Rinkai Plant by fiscal 2023, they will replace boilers that use gas and heavy oil with heat pumps that use thermal energy in the air to reduce electricity consumption. The company analyzed the uses of boilers that supply steam at temperatures above 100 degrees Celsius and focused on processes that can be replaced with hot water at temperatures below 80 degrees Celsius.
Daikin has developed a circulating heating heat pump that covers temperatures of 60-80 degrees Celsius, which was not available in previous Daikin products. A two—stage refrigerant cycle that increases the temperature enables the heating of circulating water. The equipment alone was able to reduce CO2 emission by approximately 20%, and greatly reduced heat loss during transportation through piping.
Unlike boilers, which are often used in multiple processes, heat pumps are installed in close proximity to each process. The transport distance is short, reducing heat loss, and it is easy to set the temperature for each process. In addition to painting, it is expected to have a variety of uses such as cleaning and heat retention. The average reduction is estimated to be 62% in CO2 emissions and 64% in running costs.
#Sustainability #CleanEnergy #พลังงานสะอาด #GreenFuture #Mreport #ข่าวอุตสาหกรรม
ที่มา: Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun